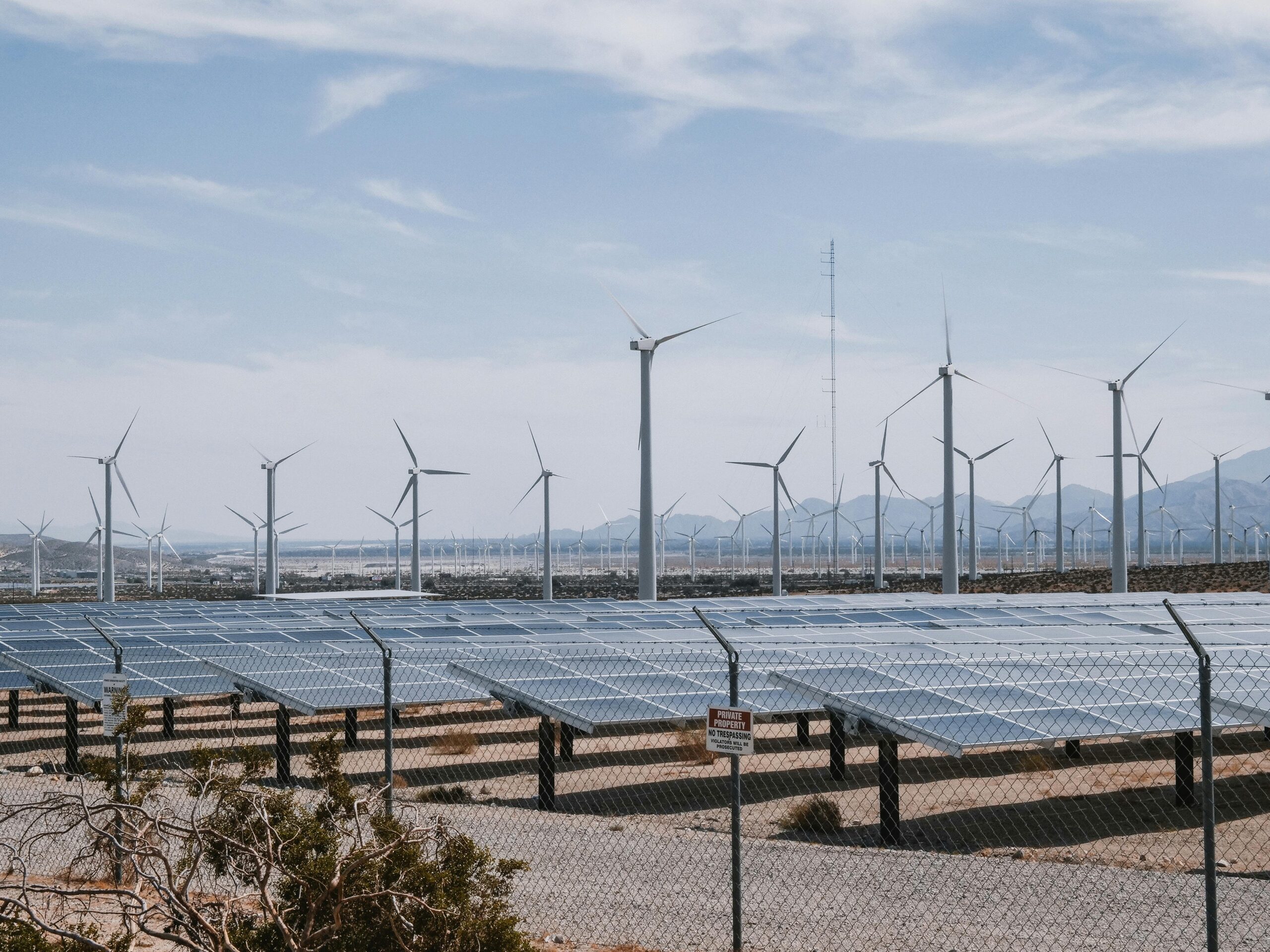
The urgency of climate change has never been more apparent, pushing businesses and innovators worldwide to reimagine how we produce, consume, and interact with our planet. This global shift toward sustainability isn’t just a trend—it’s a fundamental transformation of our economic systems.
From renewable energy breakthroughs to circular economy models, pioneering organizations are proving that profitability and environmental stewardship can coexist harmoniously. These trailblazers are creating blueprints for a greener future, demonstrating that innovative thinking combined with decisive action can tackle even the most daunting environmental challenges.
🌱 The New Paradigm of Corporate Sustainability
Traditional business models focused primarily on profit maximization often overlooked environmental consequences. Today’s leading innovators recognize that sustainable practices aren’t just ethically responsible—they’re economically advantageous. Companies implementing green initiatives are discovering reduced operational costs, enhanced brand reputation, and increased customer loyalty.
This paradigm shift extends beyond superficial greenwashing. Authentic sustainability requires systemic changes in supply chains, product design, energy consumption, and waste management. Forward-thinking organizations are embedding environmental considerations into their core business strategies rather than treating sustainability as an afterthought or marketing tool.
The business case for sustainability has become increasingly compelling. Research consistently shows that companies with strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices outperform their peers in long-term value creation. Investors are recognizing this correlation, channeling unprecedented capital toward sustainable enterprises.
Renewable Energy Revolution: Powering Tomorrow’s World
Few sectors have witnessed transformation as dramatic as energy production. Solar and wind power, once considered niche alternatives, now represent the fastest-growing energy sources globally. Companies like Ørsted, formerly known as Danish Oil and Natural Gas, epitomize this transition—transforming from a fossil fuel company into the world’s leading offshore wind developer.
Ørsted’s journey illustrates that even industries deeply entrenched in traditional energy can pivot successfully. The company divested its oil and gas operations, invested heavily in wind technology, and achieved carbon neutrality in its energy generation. This strategic repositioning not only reduced environmental impact but also improved financial performance, with stock valuations reflecting investor confidence in renewable energy’s future.
Solar Innovation at Scale ⚡
Tesla’s Solar Roof represents another breakthrough in renewable energy accessibility. By integrating photovoltaic cells directly into aesthetically pleasing roof tiles, Tesla eliminated the visual concerns that previously deterred many homeowners from adopting solar technology. This innovation demonstrates how addressing consumer preferences can accelerate sustainable technology adoption.
Beyond residential applications, utility-scale solar farms are transforming energy landscapes. Companies like NextEra Energy have deployed massive solar installations that generate electricity at prices competitive with—or lower than—fossil fuel alternatives. This cost parity marks a crucial tipping point in energy transition.
Circular Economy Champions: Redefining Waste
The linear “take-make-dispose” economy is giving way to circular models where resources circulate continuously. Leading companies are designing products for longevity, repairability, and recyclability, fundamentally challenging planned obsolescence.
Patagonia stands out as a pioneer in circular fashion. The outdoor apparel company’s Worn Wear program encourages customers to repair, share, and recycle clothing rather than discarding it. Patagonia even publishes repair guides and offers free repairs on its products, prioritizing product longevity over repeat purchases—a counterintuitive but powerful sustainability commitment.
Industrial Symbiosis Success Stories 🔄
The Kalundborg Symbiosis in Denmark exemplifies industrial ecology at its finest. This network of public and private companies exchanges resources including water, energy, and materials. One company’s waste becomes another’s raw material, creating a closed-loop system that dramatically reduces environmental impact while improving economic efficiency.
Similar initiatives are emerging globally. Interface, a modular flooring manufacturer, developed a “Mission Zero” commitment to eliminate negative environmental impacts by 2020. The company achieved remarkable results through innovations like recycling fishing nets into carpet backing and implementing carbon-negative manufacturing processes.
Sustainable Agriculture: Feeding the World Responsibly
Agriculture accounts for approximately one-quarter of global greenhouse gas emissions, making sustainable farming practices critical to climate solutions. Innovative companies and farmers are demonstrating that feeding growing populations doesn’t require environmental destruction.
Regenerative agriculture represents a transformative approach that goes beyond sustainability to actively improve ecosystems. Companies like General Mills have partnered with farmers to implement practices that enhance soil health, increase biodiversity, and sequester carbon. These techniques include cover cropping, reduced tillage, and diverse crop rotations.
Vertical Farming and Urban Agriculture 🌾
AeroFarms and similar vertical farming operations are revolutionizing food production. Growing crops in controlled indoor environments uses 95% less water than traditional agriculture, eliminates pesticide requirements, and enables year-round production regardless of climate conditions. These facilities can be located near urban centers, dramatically reducing transportation emissions.
While currently focused on leafy greens and herbs, advancing technology promises to expand vertical farming to a broader range of crops. This innovation could prove especially valuable in regions facing water scarcity or agricultural land limitations.
Transportation Transformation: Moving Beyond Fossil Fuels
The transportation sector contributes substantially to global emissions, making decarbonization essential. Electric vehicles have moved from novelty to mainstream, with virtually every major automaker committing to electrification strategies.
Beyond passenger vehicles, companies are tackling commercial transportation’s emissions. Rivian and other manufacturers are developing electric delivery vans, while Volvo and Daimler are advancing electric semi-trucks. These innovations address one of transportation’s most carbon-intensive segments.
Aviation’s Sustainable Future ✈️
Aviation presents unique decarbonization challenges due to energy density requirements. Nevertheless, innovators are pursuing multiple pathways including sustainable aviation fuels derived from waste materials, hydrogen propulsion systems, and electric aircraft for shorter routes.
Companies like ZeroAvia are developing hydrogen-electric powertrains for regional aircraft, conducting successful test flights and partnering with airlines for commercial deployment. While long-haul aviation decarbonization remains challenging, these innovations demonstrate feasible paths forward.
Green Building: Constructing Sustainable Infrastructure
Buildings consume approximately 40% of global energy and generate significant carbon emissions. Leading architects and developers are reimagining construction to minimize environmental impact while enhancing occupant well-being.
The Edge in Amsterdam exemplifies cutting-edge sustainable building design. Often called “the greenest building in the world,” it generates more energy than it consumes through extensive solar panels, utilizes aquifer thermal energy storage for heating and cooling, and employs intelligent LED lighting that adjusts to natural light and occupancy.
Sustainable Materials Innovation 🏗️
Material selection dramatically impacts building sustainability. Companies like CarbonCure are injecting captured carbon dioxide into concrete, creating a stronger product while permanently sequestering carbon. Cross-laminated timber (CLT) offers another promising alternative, providing structural capabilities similar to steel and concrete with significantly lower carbon footprints.
These material innovations demonstrate that sustainability doesn’t require compromising performance. In many cases, green alternatives offer superior properties alongside environmental benefits.
Technology Enablers: Digital Solutions for Sustainability
Digital technologies are accelerating sustainability transitions across sectors. Artificial intelligence optimizes energy consumption, blockchain enhances supply chain transparency, and Internet of Things sensors enable precision resource management.
Google’s DeepMind applied machine learning to reduce cooling energy in data centers by 40%. Given data centers’ massive energy consumption, this innovation’s cumulative impact is substantial. Similar AI applications are optimizing building management, industrial processes, and grid operations globally.
Transparency Through Technology 📱
Blockchain technology enables unprecedented supply chain visibility, allowing consumers and businesses to verify sustainability claims. Companies like Provenance use blockchain to trace products from origin to consumer, documenting environmental and social practices throughout the supply chain.
This transparency combats greenwashing while rewarding genuinely sustainable practices. As consumers increasingly prioritize ethical consumption, such verification systems become powerful market differentiators.
Financial Innovation: Directing Capital Toward Green Solutions
Sustainable finance has evolved from niche investment strategy to mainstream financial practice. Green bonds, sustainability-linked loans, and ESG investment funds are channeling trillions toward environmental solutions.
The European Investment Bank and similar development institutions are prioritizing climate finance, funding renewable energy projects, sustainable infrastructure, and green technology development. This financial architecture is accelerating the sustainability transition by making green investments increasingly attractive.
Impact Investing Growth 💰
Impact investors explicitly seek environmental and social returns alongside financial returns. This approach has grown exponentially, with major institutional investors integrating impact considerations into portfolio strategies.
Organizations like Generation Investment Management, co-founded by Al Gore, have demonstrated that sustainability-focused investment strategies can deliver competitive returns while driving positive change. This track record is attracting mainstream investors to sustainable finance.
Collaborative Approaches: Partnerships Accelerating Progress
No single organization can solve global sustainability challenges alone. Leading innovators recognize that collaboration multiplies impact, leading to unprecedented partnerships across traditional boundaries.
The Fashion Pact brings together competing brands committed to environmental goals including climate action, biodiversity restoration, and ocean protection. Similarly, the RE100 initiative unites companies committed to 100% renewable electricity, creating collective purchasing power that accelerates renewable energy deployment.
Cross-Sector Innovation Ecosystems 🤝
Innovation clusters combining startups, established corporations, research institutions, and government agencies are accelerating sustainable technology development. Silicon Valley’s Cleantech ecosystem, Europe’s energy transition initiatives, and Asia’s smart city projects demonstrate this collaborative approach’s power.
These ecosystems facilitate knowledge sharing, reduce research duplication, and create supportive regulatory environments that enable rapid innovation scaling. Governments play crucial roles by establishing frameworks that encourage private sector sustainability investments.
Measuring Impact: Beyond Carbon Metrics
Effective sustainability requires comprehensive measurement extending beyond carbon emissions. Leading organizations track diverse metrics including water usage, biodiversity impacts, circular material flows, and social equity considerations.
The Science Based Targets initiative provides frameworks for companies to set emission reduction goals aligned with climate science. Over 2,000 companies have adopted science-based targets, creating accountability and ensuring sustainability commitments translate into measurable action.
Holistic Sustainability Frameworks 📊
Frameworks like B Corp certification assess companies across multiple sustainability dimensions including governance, workers, community, environment, and customers. This comprehensive approach prevents narrow optimization that might improve one metric while neglecting others.
Similarly, the UN Sustainable Development Goals provide a universal framework connecting business activities to broader societal objectives. Forward-thinking companies align strategies with relevant SDGs, recognizing that addressing global challenges creates business opportunities.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Despite impressive innovations, sustainability transitions face significant obstacles including incumbent industry resistance, policy uncertainties, technological limitations, and behavioral inertia. Successful innovators develop strategies to navigate these challenges.
Change management represents a critical yet often underestimated aspect of sustainability transformation. Organizations like Unilever have demonstrated that engaging employees at all levels, embedding sustainability into corporate culture, and linking compensation to sustainability metrics can overcome internal resistance.
Policy and Regulatory Considerations ⚖️
Government policies profoundly influence sustainability transitions. Carbon pricing, renewable energy mandates, circular economy regulations, and green procurement policies create frameworks that either facilitate or hinder innovation.
Leading companies actively engage in policy advocacy, recognizing that supportive regulatory environments accelerate transitions. Rather than viewing regulation as constraint, sustainability leaders often welcome policies that level competitive playing fields and reward environmental leadership.
The Path Forward: Scaling Innovation Globally
The case studies explored demonstrate that sustainable innovation is not only possible but increasingly profitable and scalable. However, achieving global sustainability requires dramatically accelerating these transitions. Current progress, while encouraging, remains insufficient to meet climate and environmental goals.
Scaling requires addressing systemic barriers including technology costs, infrastructure limitations, skills gaps, and unequal access to capital. International cooperation, technology transfer, and capacity building in developing nations are essential to ensure sustainability transitions benefit all regions.
Consumer choices also significantly influence sustainability trajectories. As awareness grows and sustainable options become more accessible and affordable, consumer demand will further accelerate green innovation. Education and transparent information enable consumers to make informed choices aligned with environmental values.
Emerging Frontiers and Future Innovations 🚀
Next-generation innovations promise even greater sustainability breakthroughs. Carbon capture and storage technologies, advanced nuclear reactors, synthetic biology applications, and quantum computing optimization represent frontier areas with transformative potential.
Continued research investment, entrepreneurial experimentation, and supportive ecosystems will determine how quickly these emerging technologies achieve commercial viability. The accelerating pace of innovation suggests that solutions to current challenges are likely closer than many assume.
Inspiring a Movement: Beyond Individual Actions
The sustainability innovators profiled demonstrate that transformative change emerges from visionary leadership, strategic commitment, and persistent execution. These organizations prove that environmental responsibility and economic success are complementary rather than contradictory.
Their examples inspire broader movements, demonstrating viable pathways for others to follow. As more organizations adopt sustainable practices, network effects strengthen, costs decline, and practices that once seemed radical become industry standards.
Individual consumers, employees, investors, and citizens all play roles in this transition. Supporting sustainable businesses, demanding corporate accountability, advocating for progressive policies, and making conscious consumption choices collectively drive market transformation.
The journey toward comprehensive sustainability remains incomplete, with significant challenges ahead. However, the inspiring innovations and determined leadership profiled here provide reasons for optimism. These trailblazers are not merely adapting to environmental necessity—they’re seizing opportunities to build more resilient, equitable, and prosperous systems that work in harmony with natural systems rather than against them.
The greener future these innovators envision is becoming reality through countless decisions, investments, and actions occurring daily across industries and regions. By studying their approaches, learning from their successes and failures, and adapting their strategies to diverse contexts, we can accelerate the sustainability transition that our planet urgently requires and our descendants will inherit.
Toni Santos is a sustainability storyteller and environmental researcher devoted to exploring how data, culture, and design can help humanity reconnect with nature. Through a reflective approach, Toni studies the intersection between ecological innovation, collective awareness, and the narratives that shape our understanding of the planet. Fascinated by renewable systems, resilient cities, and the art of ecological balance, Toni’s journey bridges science and story — translating environmental transformation into insight and inspiration. His writing reveals how technology, policy, and creativity converge to build a greener and more conscious world. Blending environmental communication, data analysis, and cultural observation, Toni explores how societies adapt to change and how sustainable thinking can guide new models of coexistence between people and planet. His work is a tribute to: The harmony between data, design, and the natural world The creative power of sustainability and innovation The responsibility to rebuild our relationship with the Earth Whether you are passionate about climate innovation, sustainable design, or the science of regeneration, Toni invites you to imagine — and help create — a world where progress and nature thrive together.



